Communication is the cornerstone of development, especially in young children. As parents, educators, or speech-language pathologists, measuring this growth often involves an understanding of Mean Length of Utterance (MLU). MLU is a widely used metric to gauge linguistic progress, particularly in toddlers and young children, by calculating the average length of their spoken sentences. This tool aids in identifying speech and language delays or disorders, guiding proactive interventions. This guide is here to walk through the process of calculating MLU, ensuring it’s clear and manageable for anyone, regardless of their technical background.
Understanding MLU
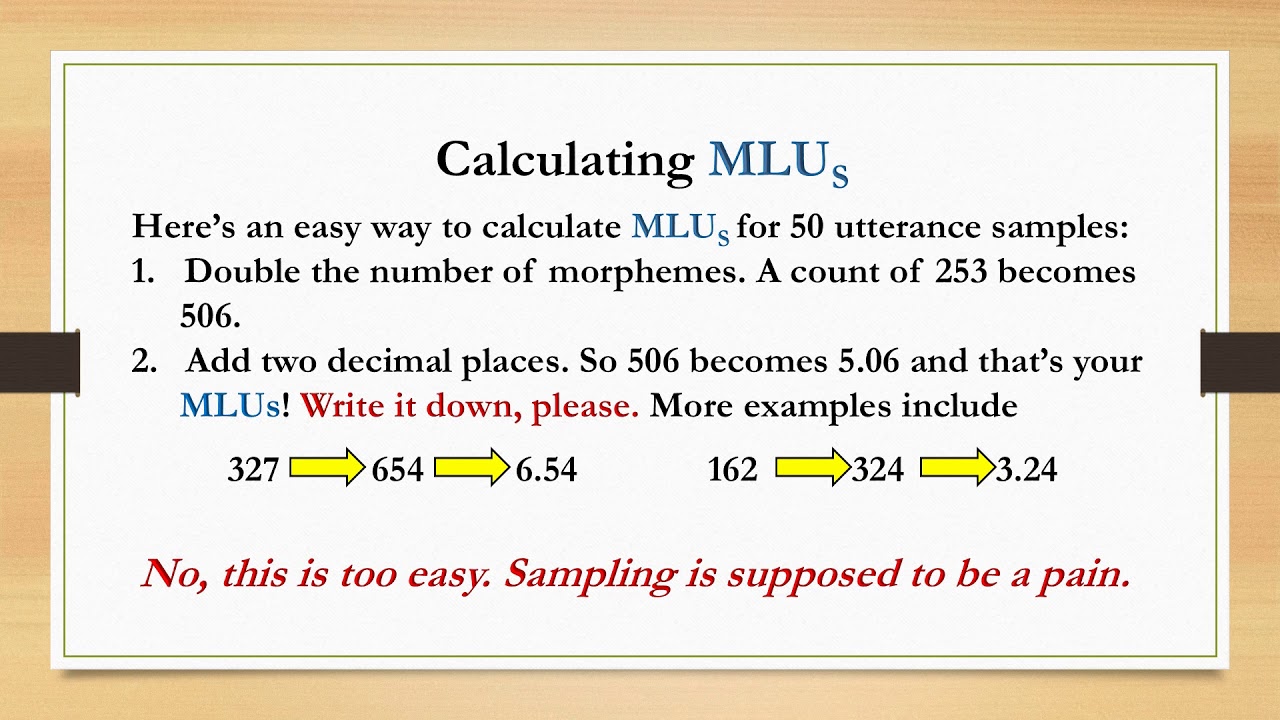
Before diving into calculations, it’s essential to understand what MLU is and its relevance. Mean Length of Utterance (MLU) is a measure used primarily by speech-language therapists to estimate the developmental level of a child’s language. The MLU is calculated by collecting a sample of spoken language, counting the morphemes (the smallest units of meaning in a language) within each utterance, and then finding the average length of those utterances.
Detailed steps:
- Collect a language sample: Record a child speaking in a natural setting. Aim for at least 100 utterances for accuracy.
- Transcribe the sample: Write down every utterance the child makes, ensuring to capture exactly what is said.
- Segment into morphemes: Break down each utterance into its smallest units of meaning, including both words and grammatical markers like -s or -ing.
- Count the morphemes: Tally the number of morphemes per utterance.
- Calculate the average: Add up the total number of morphemes and divide by the number of utterances to find the MLU.
Summary:
Understanding MLU offers a window into a child’s linguistic capabilities and can be a valuable benchmark for language development. It is a relatively straightforward process, although it can be time-consuming. One potential downside is that MLU alone may not provide a complete picture of a child’s language skills, but it is an excellent starting point.
Using Transcription Tools
Technology can aid the process of calculating MLU, especially by using transcription tools to ensure accuracy in capturing speech.
Detailed steps:
- Choose a transcription tool: Select a digital transcription tool that can accurately capture speech.
- Record the sample: Speak clearly and at a normal pace to ensure the transcription tool captures the utterances correctly.
- Review the transcript: Go through the transcript to ensure all utterances are accurately transcribed.
- Follow the steps for calculating MLU described above.
Summary:
Transcription tools can save time and improve the accuracy of language samples. However, they may not capture the nuances of speech perfectly, especially with children who have unclear articulation, and occasionally require manual corrections.
MLU in Different Contexts
Acknowledging contexts in which a child speaks can profoundly impact MLU calculations, as children often express themselves differently across situations.
Detailed steps:
- Collect samples in various contexts: Record the child speaking at home, at school, and in other environments where they spend time.
- Analyze utterances in each context: Segregate and calculate the MLU for each setting separately.
- Compare results: Note any significant differences in the MLUs from different contexts.
Summary:
Evaluating MLU across different settings can provide comprehensive insights into a child’s language abilities. A possible downside to this approach is the additional time investment required to analyze multiple samples.
Parental Involvement
Engaging parents in tracking MLU can also offer invaluable day-to-day insights into a child’s language development.
Detailed steps:
- Educate parents: Brief them on MLU and its significance.
- Provide recording guidelines: Instruct parents on how to capture their child’s speech accurately.
- Collect occasional samples: Have parents record samples every few weeks or months.
- Assistance with calculations: Help them with the MLU calculation process when needed.
Summary:
Parental involvement bolsters the data collection process by providing samples from natural interactions. However, ensuring consistency and reliability in the recordings may prove challenging.
Tracking Changes Over Time
Language development is a continuous process, so it’s helpful to consider how MLU progresses over longer periods.
Detailed steps:
- Establish a baseline: Calculate the initial MLU to serve as a reference.
- Set a timetable: Decide on intervals for reassessment (e.g., monthly).
- Record and calculate subsequent MLUs: Follow the same procedure each time.
- Analyze trends: Look for patterns or significant changes in MLU over time.
Summary:
Regularly tracking changes in MLU can highlight a child’s development and the efficacy of any interventions. It requires diligence and consistent data recording to provide a meaningful analysis.
Professional Assessment
When necessary, a professional speech-language pathologist should be consulted for a comprehensive assessment.
Detailed steps:
- Seek a referral: Talk to your pediatrician or another professional for a recommendation.
- Prepare for the assessment: Collect and bring previous MLU calculations and other relevant information.
- Understand the professional’s evaluation: Engage with the pathologist to understand their findings and recommendations.
Summary:
Professional assessments offer detailed insights and tailored strategies. However, they can be costly and may not be immediately available for everyone.
Using Mobile Apps
There are mobile applications designed to assist non-experts in tracking MLU and other speech metrics.
Detailed steps:
- Research and select an app: Look for well-reviewed apps focused on language development.
- Learn the app’s functionality: Familiarize yourself with the app’s features and how to use it.
- Record and track: Use the app consistently to record speech samples and track progress.
Summary:
Mobile apps facilitate convenient MLU tracking and data storage. Nevertheless, user error and app limitations can affect the quality and accuracy of the results.
Understanding MLU Variations
It’s important to recognize that MLU can vary for different languages and within bilingual children.
Detailed steps:
- Research MLU norms for different languages: Understand the typical MLU range for each language the child speaks.
- Adjust expectations: Calibrate your understanding based on these norms.
- Calculate MLU for each language: Use the appropriate norms to assess MLU individually for each language.
Summary:
Awareness of MLU variations can prevent misinterpretation of a child’s language abilities. However, this requires access to multilingual MLU benchmarks, which can be challenging to find.
Games and Play-Based Assessment
Incorporating play can yield more natural utterances from a child, potentially providing a more accurate reflection of their MLU.
Detailed steps:
- Choose appropriate games: Select games that encourage conversation.
- Record during play: Capture the child’s speech in a relaxed environment.
- Calculate the MLU: Use these utterances following the standard procedure.
Summary:
Play-based assessments can elicit spontaneous language, offering valuable insights into a child’s natural speech patterns. The downside is that the unstructured environment may lead to less control over the language sample quality.
Education and Training
For those regularly involved in MLU assessments, formal education or workshops on language development might be beneficial.
Detailed steps:
- Research available courses: Look for courses tailored to parents or educators.
- Attend training: Engage in workshops or seminars to build a deeper understanding of MLU.
- Apply knowledge: Use the training to improve the accuracy and efficiency of future MLU calculations.
Summary:
Educational opportunities can enhance the understanding and application of MLU. However, finding time and resources for training may be difficult for some individuals.
In conclusion, MLU remains an accessible and vital metric in understanding and supporting language development. By applying a systematic approach, even those without technical expertise can effectively utilize MLU to track progress and identify needs. Whether through traditional methods, technological aids, professional assessments, or continuous learning, the key is consistency and a nurturing environment that encourages communication for the child.
FAQs:
Q: What is an example of a morpheme?
A: A morpheme can be a single word like “cat” or a word part that changes meaning, such as the ‘s’ in “cats” indicating plural.
Q: Can MLU be used for children of any age?
A: MLU is most commonly used for children between the ages of 18 months and 4 years, as it’s a period of rapid language development.
Q: Is a higher MLU always better?
A: Not necessarily. While a higher MLU can indicate more complex language use, it’s important to also consider accuracy, clarity, and appropriateness of the child’s speech.