Windows Media Player has long been a staple for users who enjoy media on their personal computers. Whether it’s listening to music, watching videos, or viewing pictures, this versatile program has catered to a variety of multimedia needs. Over time, like any software, Windows Media Player requires updates to enhance its functionality, introduce new features, and improve security. Updating is a straightforward process, but it can sometimes get tricky for those not well-versed in navigating through their computer’s settings. This guide is designed to walk you through the various methods to update Windows Media Player, making it a simple and hassle-free experience.
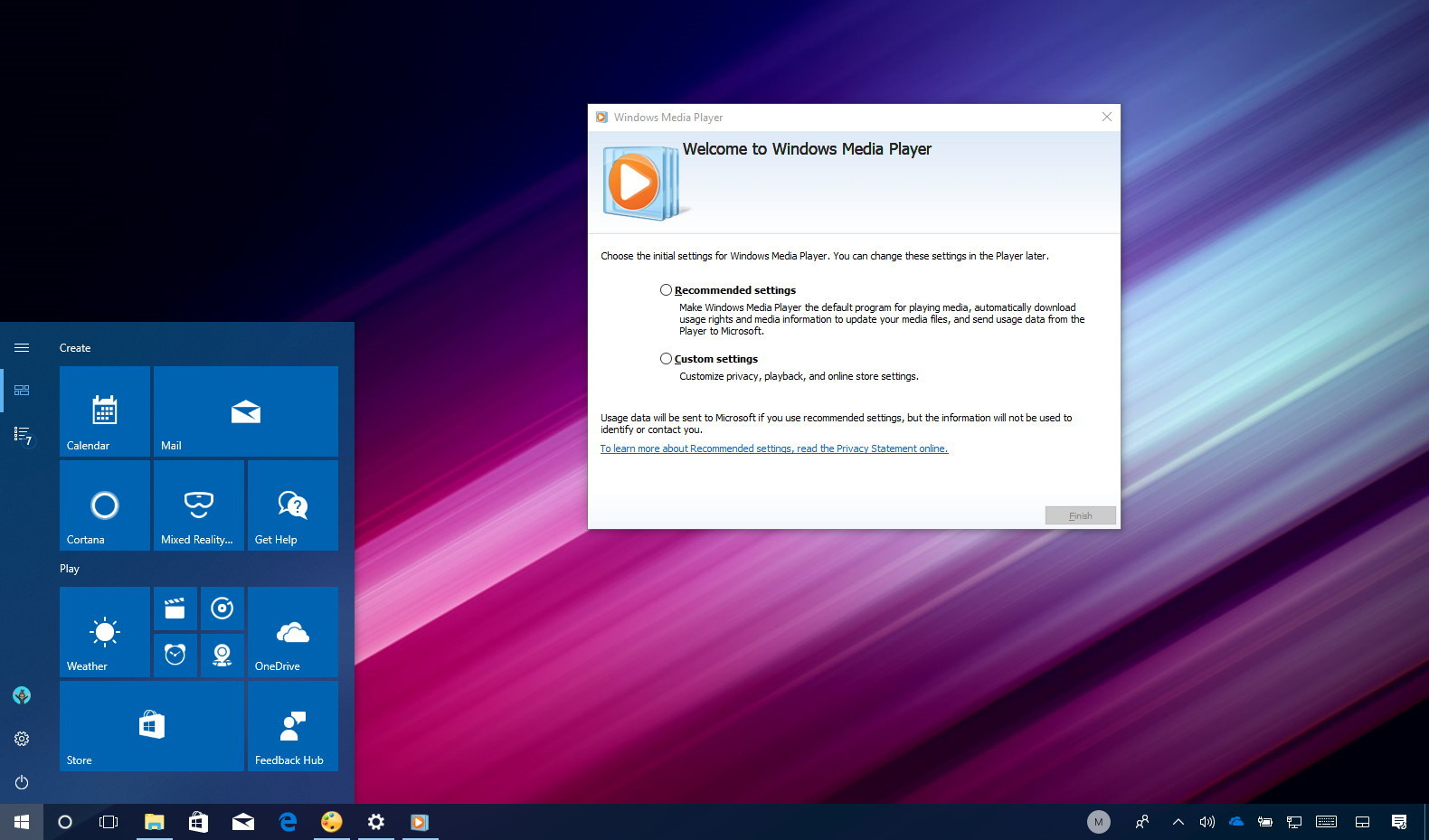
Check for Windows Updates
At times, updating Windows Media Player is as simple as running a system update for Windows itself because it often includes updates for native applications.
Detailed Steps:
- Go to Start: Click on the Start button.
- Open Settings: Click on the gear icon to open the Settings menu.
- Update & Security: Select the “Update & Security” option.
- Windows Update: Click on “Windows Update” from the sidebar.
- Check for Updates: Click the “Check for Updates” button and wait for Windows to search for updates.
- Install Updates: If updates are found, click the “Install” button to begin the process. This may include updates for Windows Media Player.
Summary:
Checking for Windows updates is the most direct way to update Windows Media Player. It ensures you have the latest security patches and performance enhancements for not just the media player, but your entire operating system. However, this method is dependent on the overall update schedule for Windows, which may not always address specific needs for Windows Media Player.
Download Media Player Update Manually
If automatic updates do not apply the changes you need, consider manually downloading the specific update for Windows Media Player.
Detailed Steps:
- Visit the Microsoft Download Center: Open your web browser and navigate to the Microsoft Download Center.
- Search for Windows Media Player: Enter “Windows Media Player” in the search bar.
- Select the Correct Version: Make sure you select the correct version that corresponds with your Windows operating system version.
- Download: Click the “Download” button for the update.
- Run Installer: Once the download is complete, open the file and run the installer, following the on-screen instructions.
Summary:
Manual updates give you more control over what gets installed on your computer. This method is especially useful if you need a particular version of Windows Media Player or if the automatic update feature is not working correctly. However, it requires a bit more initiative, and there’s a slight risk of downloading the incorrect version if you’re unsure of your system details.
Troubleshoot Windows Media Player
Sometimes, the issue might not be with the update process, but with the application itself. Running the troubleshooter can resolve these issues.
Detailed Steps:
- Access Control Panel: Open the Start menu and type “Control Panel,” then press Enter.
- Troubleshooting: Click on “Troubleshooting.”
- View All: On the left-hand panel, click on “View all.”
- Windows Media Player Settings: Scroll down to find “Windows Media Player Settings” and click on it.
- Run the Troubleshooter: Follow the on-screen prompts to run the troubleshooter.
Summary:
Troubleshooting can automatically detect and fix problems with Windows Media Player. It’s beneficial for non-technical users as it simplifies resolving common issues with the player. While effective for minor glitches, it may not solve all problems, especially more serious issues that may require more technical solutions.
Reinstall Windows Media Player
If your Windows Media Player is giving you persistent problems, sometimes starting fresh with a reinstalation is the best course of action.
Detailed Steps:
- Access Windows Features: Open the Start menu, type “Turn Windows features on or off,” and press Enter.
- Find Media Features: Scroll through the list and locate “Media Features,” then expand it.
- Uncheck Windows Media Player: Find and uncheck “Windows Media Player.”
- Confirm: Click “Yes” to confirm, then “OK” to remove Windows Media Player.
- Restart Your Computer: This change requires a reboot to take effect.
- Re-enable Windows Media Player: Repeat steps 1-2, this time rechecking “Windows Media Player.”
- Restart Again: Reboot your computer one more time to complete the reinstallation.
Summary:
Reinstalling Windows Media Player can help overcome stubborn issues and start with a clean slate, potentially resolving unaddressed problems. It’s a more drastic step, which may be intimidating for non-technical users, and you might need to reconfigure settings or reinstall codecs afterwards.
Set Windows Media Player as Default
Ensuring Windows Media Player is set as the default media application may indirectly help with update issues, as it prompts Windows to prioritize updates for it.
Detailed Steps:
- Open Settings: Press the Start button and click the gear icon to access Settings.
- Apps: Click on “Apps.”
- Default Apps: Select “Default apps” from the sidebar.
- Choose Default Apps by File Type: Scroll down and click on “Choose default apps by file type.”
- Set Defaults: Find the file types associated with media (like .mp3, .mp4, .wmv) and set Windows Media Player as the default app.
Summary:
Setting Windows Media Player as the default can streamline your media experience and may prioritize the player in update cycles. However, changes in default settings will not directly trigger an update to the media player; it only affects file associations.
Update Codecs
Sometimes, the issue isn’t with Windows Media Player itself, but with the codecs it uses to play media. Updating these can improve performance and compatibility.
Detailed Steps:
- Research Required Codecs: Determine which codecs are needed for the media files you are using.
- Download Codecs: Visit the Microsoft Download Center or verified codec vendor sites and download the appropriate codecs.
- Install Codecs: Open the downloaded file and follow the installation prompts.
- Restart Windows Media Player: Close and reopen Windows Media Player for the new codecs to take effect.
Summary:
Updating codecs can solve playback issues and is relatively straightforward, but caution is advised, as downloading codecs from unverified sources can be a security risk.
Use Windows Media Player Troubleshooters
Windows includes built-in troubleshooters that can fix common problems with Windows Media Player.
Detailed Steps:
Refer back to the earlier solution titled “Troubleshoot Windows Media Player” for the detailed steps.
Summary:
The troubleshooters are user-friendly tools for fixing common issues, but they might not solve all problems, especially those related to outdated software components.
Restore to Default Settings
Reverting Windows Media Player to its default settings can resolve conflicts that prevent updates.
Detailed Steps:
- Open Windows Media Player: Access the player via its shortcut or search for it from the Start menu.
- Go to Tools: Click on “Tools” in the menu (if the menu bar is not visible, press Alt to reveal it).
- Options: Select “Options.”
- Reset to Default: In the Options menu, go to the “Privacy” or “Security” tab and find the reset options.
- Apply Changes: Confirm the action and click “OK” to apply changes.
Summary:
Restoring default settings can provide a clean base for updates to apply correctly. This may result in a loss of personalized settings, which you’ll need to reconfigure.
Turn Off and On Media Streaming
Sometimes, enabling or disabling media streaming can prompt Windows Media Player to reset certain configurations, potentially smoothing out update processes.
Detailed Steps:
- Open Windows Media Player: Search for it from the Start menu and click on its icon.
- Go to Stream: In Windows Media Player, click on “Stream” on the toolbar.
- Enable or Disable Media Streaming: Choose the appropriate option to either turn on or off media streaming.
- Apply: Click “OK” or “Turn on media streaming” to confirm.
Summary:
This can be an easy toggle to refresh Windows Media Player’s streaming settings, which may indirectly facilitate better updating. It’s non-invasive and unlikely to cause issues but its effectiveness for update problems can be uncertain.
Create a New User Account
Creating a new Windows user account can sometimes get around issues preventing updates to Windows Media Player.
Detailed Steps:
- Access Accounts Settings: Click on the Start button, then the gear icon, and choose “Accounts.”
- Add a New User: Click on “Family & other users,” then “Add someone else to this PC.”
- Set Up New Account: Follow the prompts to create a new account, either by logging into a Microsoft account or creating a new one.
- Switch to the New User: Sign out of your current account and sign into the new one to see if Windows Media Player updates properly here.
Summary:
This is a more general troubleshooting step that can resolve user-specific problems, potentially resolving update issues. It might be inconvenient due to the need to transfer files and settings to the new user account.
Consult the Official Support
When all else fails, reaching out to Microsoft’s official support can give you personalized assistance.
Detailed Steps:
- Visit Microsoft Support: Use your web browser to visit the official Microsoft Support website.
- Search for Help: Enter “Windows Media Player update” in the search field and review the provided solutions.
- Contact Support: If necessary, get in touch with support through the options provided on the site (live chat, call, or email).
Summary:
Direct support from Microsoft can be invaluable when you hit a dead end. The downside is you may have to wait for assistance, depending on their availability and response times.
Conclusion:
Keeping Windows Media Player up-to-date is important for ensuring the best performance and security. While the update process should be straightforward, issues can sometimes arise. This comprehensive guide has outlined multiple solutions, ranging from simple checks for Windows updates to more involved troubleshooting steps such as reinstalling the player or contacting official support. Remember that keeping your software updated goes hand in hand with maintaining the security and functionality of your system.
FAQs:
-
How do I know if my Windows Media Player is up to date?
- You can check for updates via the Windows Update section in your system’s settings. If your system is set to automatically update, it should be current. Otherwise, follow the steps provided to check manually.
-
Can updating Windows Media Player improve playback performance?
- Yes, updating can resolve bugs, improve compatibility with media files, and enhance playback performance.
-
What should I do if I can’t update Windows Media Player through Windows Update?
- Try the other solutions mentioned in this guide, such as manually downloading the update from Microsoft Download Center, troubleshooting, or reaching out to official support for help.