In a world brimming with devices that connect us, every piece of equipment on a network is uniquely identifiable. Think of an IP address as a telephone number for your computer; it’s how the internet knows where to send emails, pictures, and requests. Just as every phone has a unique serial number, or IMEI, computers have a MAC address that serves as a permanent identifier. But how do these two connect? When troubleshooting network problems or securing your Wi-Fi, you might need to find the MAC address associated with a particular IP address. This guide will walk you through this process, demonstrating various methods to bridge the gap between these crucial pieces of information.
ARP Lookup
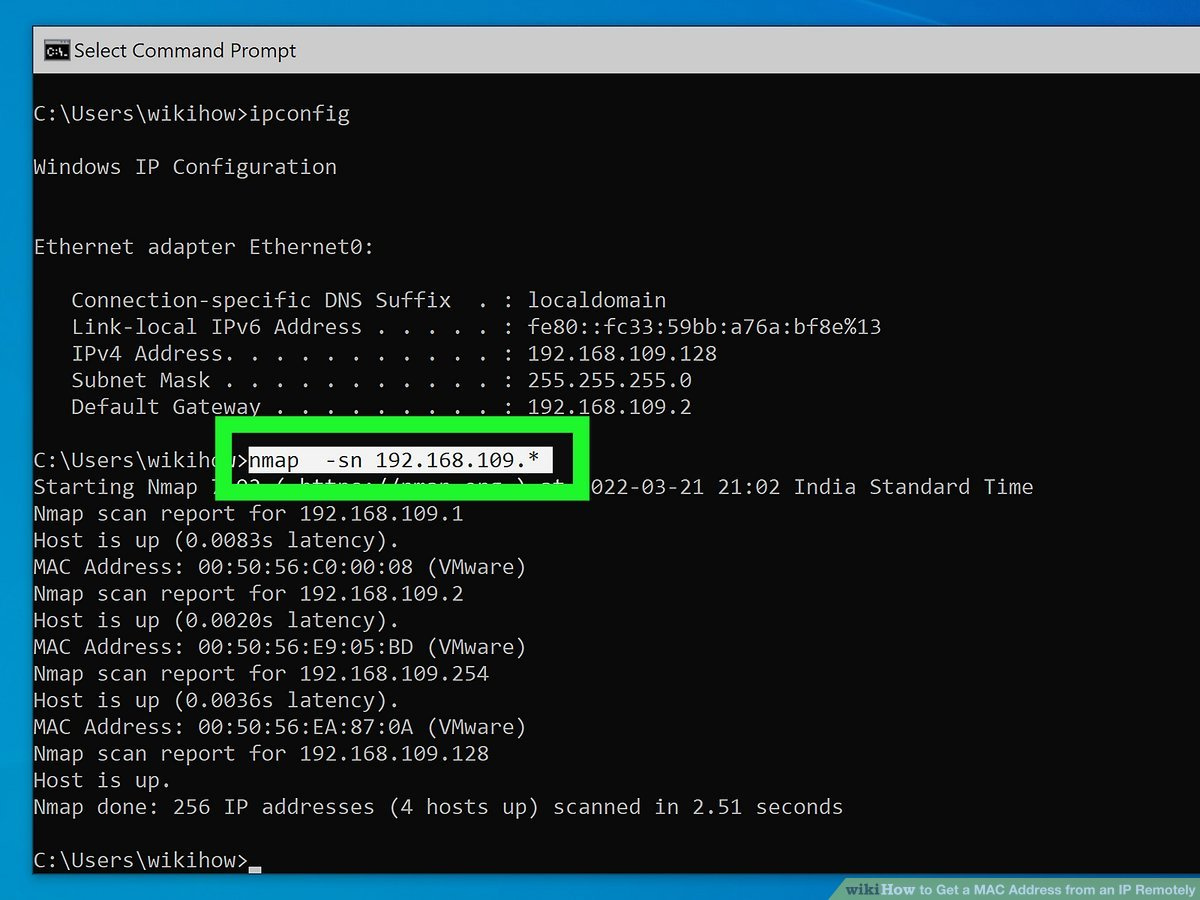
If you’re investigating devices on your local network, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is your starting point. Every computer maintains a table that maps the IP addresses of connected devices to their corresponding MAC addresses. Think of ARP like a party planner’s guest list, where the planner needs to check guests off as they arrive.
- Open the Command Prompt on a Windows computer by typing
cmdinto the search bar and pressing Enter. - Once Command Prompt opens, type the command
arp -aand press Enter. - Look through the results for the IP address you’re interested in. Next to it should be the matching MAC address.
Summary: Using ARP is swift and efficient for local networks. It’s like peeking into the guest list — easy and quick. However, this method doesn’t work for remote devices that aren’t on your local network.
Router’s Interface
Another method of discovery is through your router, the maestro orchestrating the network symphony. Modern routers keep a detailed list of devices connected to them, including their IP and MAC addresses.
- Access your router’s web interface using a browser. Usually, you’ll type
192.168.1.1,192.168.0.1, or another IP address specific to your router. - Enter the username and password to log into your router. This info might be on a sticker on the router itself.
- Navigate the interface to find a section labeled “Attached Devices,” “Device List,” or similar.
- Locate the IP address in question and read off the corresponding MAC address.
Summary: Checking your router’s interface is relatively straightforward and gives a complete view of your local network. However, navigating the interface can be daunting for novices, and the steps might vary based on the router’s make and model.
Network Scanning Tools
For a more automated approach, network scanning tools come in handy. Programs like Advanced IP Scanner or Angry IP Scanner can map out your network for you.
- Download and install a trusted network scanning tool.
- Run the program and initiate a scan.
- Once the scan completes, look for the IP address of interest to find the MAC address.
Summary: These tools are powerful and user-friendly for scanning large networks and require minimal technical knowledge. The downsides are that downloading and installing software may be intimidating for some users, and there can be security risks with free tools.
PowerShell
PowerShell is a more potent version of the Command Prompt and can also be used to find a MAC address.
- Open PowerShell by typing it into the search bar and pressing Enter.
- Enter
Get-NetNeighbor -IPAddress x.x.x.x, replacing x.x.x.x with the IP address you’re searching for. - The MAC address should be listed in the output.
Summary: PowerShell is a robust method for those comfortable with command-line interfaces and gives you detailed network information. It may, however, be too complex for the average user.
Wireshark
Wireshark is a professional-grade network protocol analyzer. It lets you see what’s happening on your network at a microscopic level.
- Download and install Wireshark from their official website.
- Start capturing traffic on your network.
- Look for packets coming from the IP address in question to find the MAC address.
Summary: Wireshark offers an extremely detailed view and is great for education and troubleshooting. Its complexity makes it best suited for those with some technical understanding.
Manufacturer Databases
Sometimes, you might only have the MAC address and need to determine the manufacturer. MAC addresses are uniquely assigned to manufacturers, so you can often find out who made the device by looking up the first few characters.
- Note down the first three sets of characters from the MAC address.
- Use an online MAC address lookup tool like MAC Vendors to input the characters.
- The tool will typically return the manufacturer’s name.
Summary: This can be useful for identifying unknown devices on your network. These tools are generally straightforward, though they don’t provide direct network configuration information.
Online IP to MAC Tools
There are online tools designed to map IP addresses to MAC addresses, but these generally work only for IPs that have interacted with the website or service.
- Find a reputable online IP to MAC tool.
- Enter the IP address you’re curious about.
- The tool will return a MAC address if it has that data stored.
Summary: Online tools can be quick and require minimal effort, but they rely on databases that may not have the data for the IP address in question.
Checking Local Device Settings
Most devices allow you to check their network settings to find both the IP and MAC addresses from the device itself.
- Navigate to the network settings on the device.
- Look for the status or information section.
- Write down the MAC address associated with the IP address listed.
Summary: This is a simple and direct method; however, it requires physical access to the device and some navigation through settings.
Contacting Your Internet Service Provider (ISP)
If you’re trying to identify a MAC address for a device that’s outside your local network but goes through your ISP, they might be able to help.
- Contact your ISP’s customer support.
- Provide them with the IP address you’re interested in.
- Ask if they can provide the MAC address associated with the IP.
Summary: ISPs have access to more detailed network data and might be able to assist in exceptional cases. Privacy laws and company policies could limit the information they can provide.
Network Administrator
For corporate or educational networks, the network admin is likely the gatekeeper of MAC addresses.
- Reach out to your network administrator.
- Provide the IP address of the device you’re investigating.
- Request the MAC address information.
Summary: Network administrators can provide accurate data, but this route may not be immediate, and you might need a valid reason for your request.
In conclusion, while identifying a MAC address from an IP can sometimes seem like deciphering a digital fingerprint, the multitude of available methods means there’s usually one that fits your level of technical comfort and access rights. Whether it’s consulting the digital ledger of ARP, exploring your router’s interface, harnessing the capabilities of network scanning software, or enlisting the help of an administrator, each approach offers a unique path to the information you seek. Remember, patience and a step-by-step assessment of your options are crucial in navigating the junction of IPs and MACs.
FAQs
-
Can I find the MAC address of a device that’s not on my local network?
Generally, you can only find the MAC address of a device that is part of your local network. MAC addresses are designed to be used as an identifier on a local area network (LAN). When data leaves your network, the MAC address information is typically not included. -
Is it safe to use online IP to MAC tools?
It can be safe to use online tools, but you should always make sure they are reputable. Remember that inputting any data online carries a risk, so be cautious about the information you share. -
Why can’t I find the MAC address for an IP address using ARP?
If the device with that IP address hasn’t communicated with your device recently or it’s on a different network segment, it might not show up in your ARP table. Additionally, some devices might have privacy features that prevent them from being discovered in this way.