In the world of digital marketing, understanding how your marketing efforts convert into sales or leads is crucial for making informed decisions. This is where attribution models come in, with the linear attribution model being one such approach that attempts to give credit to all touchpoints in a customer’s journey toward a conversion. It’s a democratic way of analyzing which parts of your marketing strategy are working, rather than putting all the emphasis on just one moment. Let’s explore how the linear attribution model divvies up the credit and provides insights for marketers.
The Concept of Touchpoints
When a customer interacts with various marketing elements before making a purchase, these interactions are known as touchpoints. For example, a customer might see a banner ad, click on a social media post, and read an email before finally making a purchase. Each of these interactions plays a role in influencing the customer’s decision.
Detailed Introduction
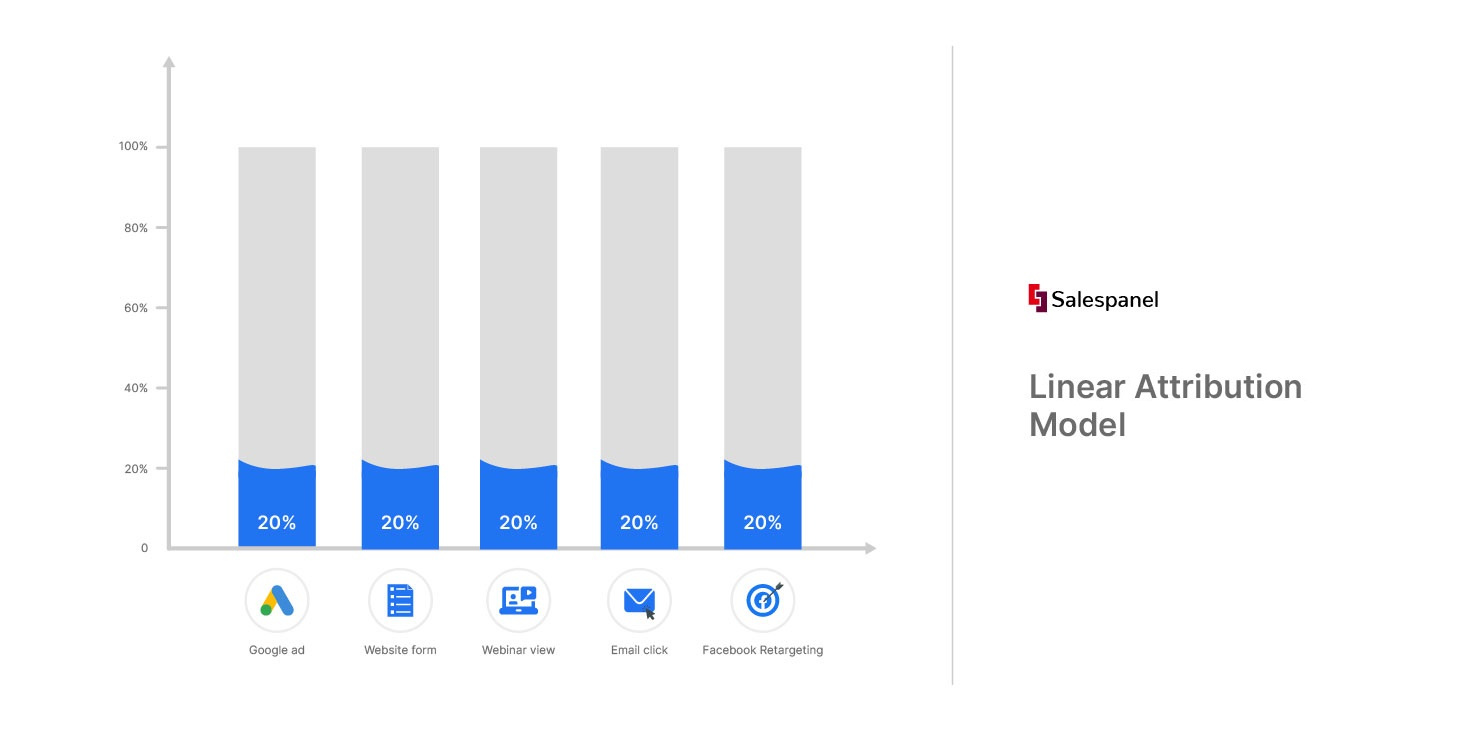
The linear attribution model operates on the principle that every touchpoint in the customer’s journey should receive equal credit for the end conversion. Instead of attributing the sale or conversion to just the first or last interaction, this model acknowledges the complexity of consumer behavior and spreads the credit across all touchpoints that led to the conversion.
Detailed Steps
- Identify all the touchpoints: Begin by listing every marketing channel and interaction that led up to the conversion.
- Count the touchpoints: Determine how many touchpoints the customer experienced during their journey.
- Assign equal credit: Divide 100% of the conversion value equally among all the touchpoints.
- Aggregate the data: Collect this information over a period to see which channels are consistently involved in conversions.
- Analyze the model: Use the data to understand how the removal or adjustment of certain channels might affect overall conversions.
Summary
This model is beneficial for recognizing the value of every marketing effort, but it may not provide insights into which touchpoints are most influential. Brands that have a multi-faceted marketing strategy often use the linear model to avoid undervaluing any single channel.
Engagement Across Multiple Channels
In a multi-channel marketing strategy, understanding how each channel contributes to conversions is vital. An email campaign, for instance, might not be the final interaction before a purchase, but it could have been a critical influence on the decision-making process.
Detailed Introduction
In this context, the linear attribution model shines by illustrating the impact of consistent messaging across various channels. It shows how maintaining a presence on multiple platforms can work together to guide a customer down the sales funnel.
Detailed Steps
- Track engagement across all channels: Monitor how users interact with your brand, whether through paid ads, social media, or direct emails.
- Compare engagement with conversion data: Look at which channels were engaged with prior to conversions.
- Recognize patterns: Notice if certain combinations of channel engagements tend to lead to conversions more frequently.
- Adjust marketing efforts: Use these insights to refine the content and strategy across different channels.
Summary
This approach ensures that no channel is discounted but may require a larger dataset to truly understand the impact each channel has on the journey to conversion.
Campaign Performance Assessment
Marketing campaigns are essential investments, and assessing their performance is crucial for future planning and budget allocation.
Detailed Introduction
The linear attribution model can help in understanding how each element of a campaign cooperates towards conversions. It prevents the overshadowing of less immediately impactful but still essential touchpoints.
Detailed Steps
- Monitor campaign touchpoints: Keep a close record of each campaign interaction across different channels.
- Calculate campaign influence: Use the linear model to distribute credit for every campaign-driven conversion equally across these touchpoints.
- Benchmark against goals: Evaluate if the campaign is meeting its predefined objectives through this distributed attribution.
- Refine campaigns: Make data-driven decisions to improve the campaign elements based on the attribution insights.
Summary
With this model, you get a fair assessment of each campaign element, though it doesn’t highlight which part was pivotal in the decision-making process.
Timeframe Analysis
In marketing, timeframe or seasonality can have a huge impact on consumer behavior and conversions.
Detailed Introduction
By applying the linear attribution model over different timeframes, such as holidays or sale periods, businesses can gauge if and how these periods affect the overall effectiveness of their marketing channels.
Detailed Steps
- Segment data by timeframe: Break down conversion data by specific durations you want to analyze.
- Apply the linear attribution model: Distribute credit across touchpoints within these timeframes.
- Compare different timeframes: Look for shifts in channel performance during different seasons or sales events.
Summary
This helps businesses understand how seasonality affects their sales, but it does not consider consumer behavioral changes over these periods.
Optimization of Marketing Mix
A well-balanced marketing mix is essential for reaching potential customers effectively.
Detailed Introduction
The linear attribution model allows businesses to see how altering the composition of their marketing mix might affect conversions. It treats each marketing effort equally, respecting the role of various channels.
Detailed Steps
- Define the current marketing mix: Understand how your budget is allocated across different channels.
- Apply the linear model: Use it to give a broad understanding of how each channel contributes.
- Adjust your mix: Based on this model, tweak your marketing budget to optimize the mix.
- Monitor the results: Keep track of how these changes affect overall conversion rates.
Summary
This can lead to a more efficient allocation of marketing resources, though it may not capture the dynamic complexities of how different channels interact with each other.
Consumer Journey Mapping
Recognizing each step of a consumer’s path can vastly improve marketing strategies.
Detailed Introduction
The linear model aids in creating a visual representation of a typical customer’s journey, allowing marketers to see how various touchpoints lead to a conversion.
Detailed Steps
- Map out the customer journey: Identify all potential interactions from the first contact to conversion.
- Apply equal value: Use the linear attribution model to assign equal credit to each of these steps.
- Visualize the journey: Create a chart or diagram to represent this journey and the corresponding credit distributed.
Summary
Mapping out the journey can provide a comprehensive overview while teaching us that there are multiple factors at play that influence consumer behavior.
Digital Attribution Software Utilization
Digital attribution software can automatically apply the linear model to your marketing data.
Detailed Introduction
For marketers who are not data analysts, using software that seamlessly integrates with your systems and applies the linear attribution model can save both time and resources.
Detailed Steps
- Research attribution software: Look for tools that support the linear model and fit your business needs.
- Integrate your data sources: Connect your marketing channels to the software for data collection.
- Let the software analyze: The tool will automatically distribute credit across touchpoints.
- Interpret the results: Use the insights provided by the software to make informed marketing decisions.
Summary
This saves time but can be costly, and relying solely on software might mean missing out on nuanced insights.
Cross-Device Tracking Challenges
The modern customer journey often involves multiple devices, and tracking this can be complex.
Detailed Introduction
Attribution across devices is difficult because a customer might see an ad on mobile but convert on a desktop. The linear attribution model helps by equally crediting each touchpoint regardless of the device.
Detailed Steps
- Implement a cross-device tracking solution: This should capture user interactions across devices.
- Distribute credit across devices: Equal credit is assigned to touchpoints regardless of where they occur.
- Review the cross-device journey: Understand how different devices play a role in the customer journey.
Summary
This model simplifies the chaos of multi-device interactions but doesn’t capture the significance of the primary device in the conversion process.
Understanding Cross-Channel Influence
Customer journeys are rarely confined to a single marketing channel.
Detailed Introduction
The linear attribution model can shine a light on how channels influence each other. For example, social media might drive traffic to a blog, which leads to a newsletter sign-up and, eventually, a conversion.
Detailed Steps
- Analyze cross-channel interactions: Keep tabs on customers’ paths across channels.
- Apply the linear model: See how credit distribution reflects the interconnected role of channels.
- Identify channel synergies: Look for patterns where channel interactions are consistently followed by conversions.
Summary
Recognizing such synergies is useful, even if the model doesn’t tell you which channel is the strongest driver.
Incorporating Customer Feedback
Direct feedback from customers can be incorporated into the attribution analysis.
Detailed Introduction
Surveys or feedback forms can provide insights into which touchpoints customers perceive as impactful, complementing the data from the linear attribution model.
Detailed Steps
- Collect customer feedback: Use surveys to ask customers about the touchpoints they recall.
- Correlate with linear model data: Compare this feedback with the even distribution of credit from the model.
- Adjust touchpoint emphasis: Consider giving more weight to touchpoints frequently mentioned by customers.
Summary
While valuable, this approach is subjective and depends on customers accurately recalling their journey.
Conclusion
Understanding the linear attribution model is vital for marketers wanting to fairly evaluate their marketing channels. It’s a model that promotes inclusivity across all touchpoints, yet simplicity is both its strength and weakness. Incorporated with an overarching analytic strategy, the linear model can offer invaluable insights, helping to shape a balanced and effective marketing approach.
FAQs:
-
What is a touchpoint in marketing?
A touchpoint refers to any interaction a customer has with your brand or marketing efforts on their path to a purchase or conversion. -
Why is the linear attribution model considered ‘democratic’?
The linear model is democratic because it assigns equal credit to each touchpoint involved in the consumer’s journey, acknowledging the contribution of all marketing efforts. -
How does the linear attribution model work with online and offline marketing channels?
It takes all touchpoints into account, so both online ads and offline interactions like store visits or physical mailers would each get an equal share of the credit for any sales made.