Chromatography is a science used to separate and analyze compounds in a mixture. One important aspect of chromatography is calculating the retention factor, commonly referred to as the Rf value. This is a way to quantify the movement of a substance through the chromatography medium, helping to identify or characterize the substance. Even if you are new to chromatography, understanding how to calculate Rf values is essential for interpreting your results accurately.
Understanding Baseline Measurements
Before delving into the calculations, it’s important to understand baseline measurements. In chromatography, starting correctly is key to getting accurate results. A baseline measurement is the starting line from which your substances will move.
Detailed Steps:
- Set up the chromatography system according to the specific instructions for your equipment.
- Mark a line on the chromatography paper or plate as the origin where your sample will be applied.
- Run the experiment to separate the substances in your mixture.
- When the chromatography is complete, mark the solvent front, which is the farthest point reached by the solvent.
Summary:
Measuring baselines is crucial for accuracy. However, if the baseline is not marked properly, it could lead to incorrect Rf calculations.
Spotting the Components
Each component in your mixture will travel a different distance from the baseline. Identifying these spots is the next step in calculating Rf values.
Detailed Steps:
- Once the chromatography run is complete, remove the chromatography paper or plate.
- Under proper lighting or using a UV light, mark the center of each spot that represents a separate component in your sample.
- Measure the distance each spot traveled from the baseline, known as the distance traveled by the solute (D_s).
Summary:
Spotting is a simple process, but misidentifying spots can lead to inaccurate Rf values.
Identifying the Solvent Front
After you’ve identified the components, you’ll need to find how far the solvent traveled. This is crucial for Rf calculations.
Detailed Steps:
- Measure from your baseline to the solvent front, which is the farthest point reached by the solvent (D_f).
- Record the distance traveled by the solvent accurately.
Summary:
Precision in measuring the solvent front ensures reliable Rf values, but an imprecise measurement could invalidate your experiment’s result.
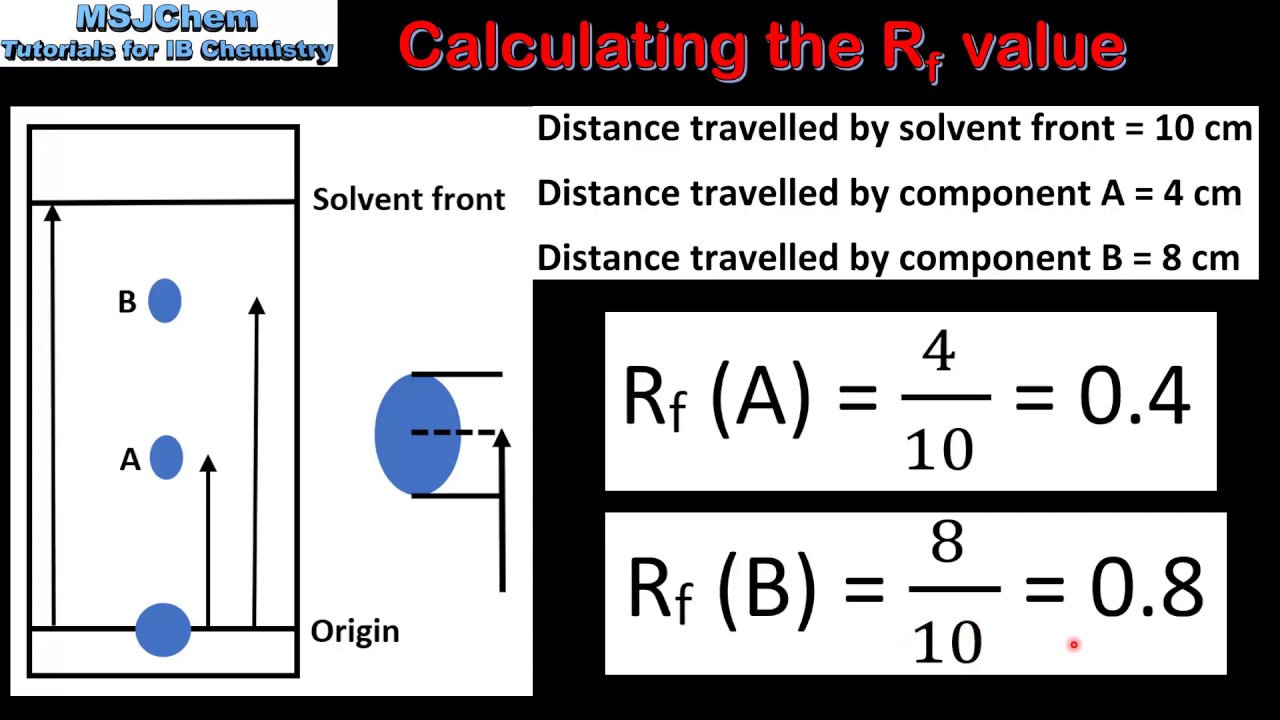
The Rf Calculation
With the previous measurements, calculating the Rf value for each component is straightforward.
Detailed Steps:
- Divide the distance traveled by the solute (D_s) by the distance traveled by the solvent (D_f) for each component.
- The formula for Rf value is Rf = D_s/D_f.
Summary:
Calculating the Rf value is simple mathematics, but the clarity in measurements is the key to reliable Rf values.
Repeating for Accuracy
To ensure the Rf values are accurate, it’s advised to repeat the chromatography process.
Detailed Steps:
- Prepare additional samples and run them through the chromatography process.
- Calculate the Rf values for each run and compare.
Summary:
Repetition can confirm the consistency of your Rf values, though it requires more time and resources.
Documentation
Keeping precise records is critical for any scientific process, including chromatography.
Detailed Steps:
- Record all measurements meticulously, including the distance traveled by the spots and the solvent front for each trial.
- Note any deviations or anomalies during the process.
Summary:
Good documentation practices improve the reliability of your findings but can be time-consuming.
Analyzing the Results
After calculating the Rf values, the next step is analyzing what these numbers mean.
Detailed Steps:
- Compare the Rf values with known standards or literature values to help identify the components in your mixture.
- Consider the characteristics of the solvent system and the medium used when interpreting the Rf values.
Summary:
Analysis provides insights into the identity and properties of the components but requires knowledge of what these values represent.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Awareness of common pitfalls can improve your technique and results when calculating Rf values.
Detailed Steps:
- Ensure the chromatography paper or plate is not oversaturated with the solvent.
- Ensure consistent temperature and humidity conditions throughout your experiments.
Summary:
Avoiding mistakes leads to more reliable data but requires diligence and an understanding of best practices.
Effect of Solvent Choice
Different solvents can affect the Rf values of your components differently.
Detailed Steps:
- Choose an appropriate solvent for the properties of the components in your mixture.
- Record how different solvents affect the Rf values of your components.
Summary:
The right solvent choice can enhance the separation of components, but finding the optimal solvent may require experimentation.
Fine-Tuning Your Technique
Improving your chromatography technique can lead to better separation and more accurate Rf values.
Detailed Steps:
- Apply your samples in small, concentrated spots rather than large drops.
- Ensure even development of the chromatogram by preventing disruptions such as air drafts.
Summary:
Technique refinement leads to better resolution in your results, although it requires practice and attention to detail.
Educating Yourself Further
Expanding your knowledge through further education can vastly improve your chromatography skills.
Detailed Steps:
- Read scientific literature and publications on chromatography.
- Attend workshops or webinars to learn from experts in the field.
Summary:
Continued learning can provide deeper insights into the science of chromatography but requires a commitment to ongoing education.
In conclusion, the calculation of Rf values is a fundamental skill in chromatography, essential for identifying and characterizing the components within a mixture. The process is simple once you understand the basic steps and measurements involved. Begin with accurate baselines, identify spots correctly, and measure distances precisely. Remember that the true value of Rf calculation lies in its ability to offer reproducible and reliable data for scientific inquiry. By meticulously following the steps and taking note of the summarized tips and potential pitfalls, even those new to chromatography can achieve useful and accurate results.
FAQs:
-
What does Rf stand for in chromatography?
Rf stands for retention factor, which represents how far a compound moves in the chromatography medium relative to the solvent front. -
Why is it necessary to calculate Rf values in chromatography?
Rf values help in identifying and comparing compounds based on their movement through the chromatography medium, giving insight into their characteristics. -
Can Rf values be the same for two different compounds?
Yes, it’s possible for different compounds to have the same Rf values under certain conditions, which is why additional analyses are often required for definitive identification.